AI Inference: From Input to Output
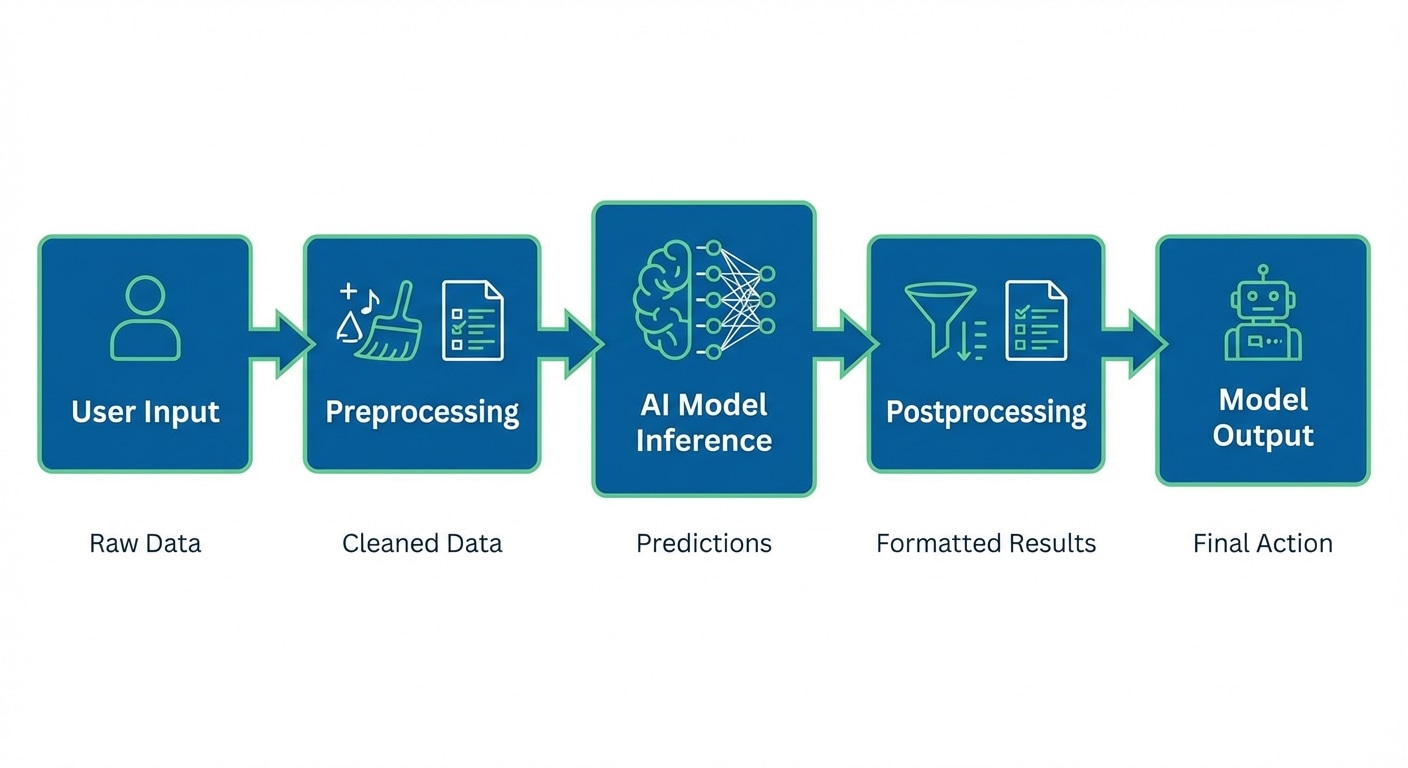
Inference is when a trained model makes predictions on new data. While training happens once, inference runs millions of times in production. Understanding the inference pipeline is crucial for deploying AI systems that are fast, efficient, and reliable.
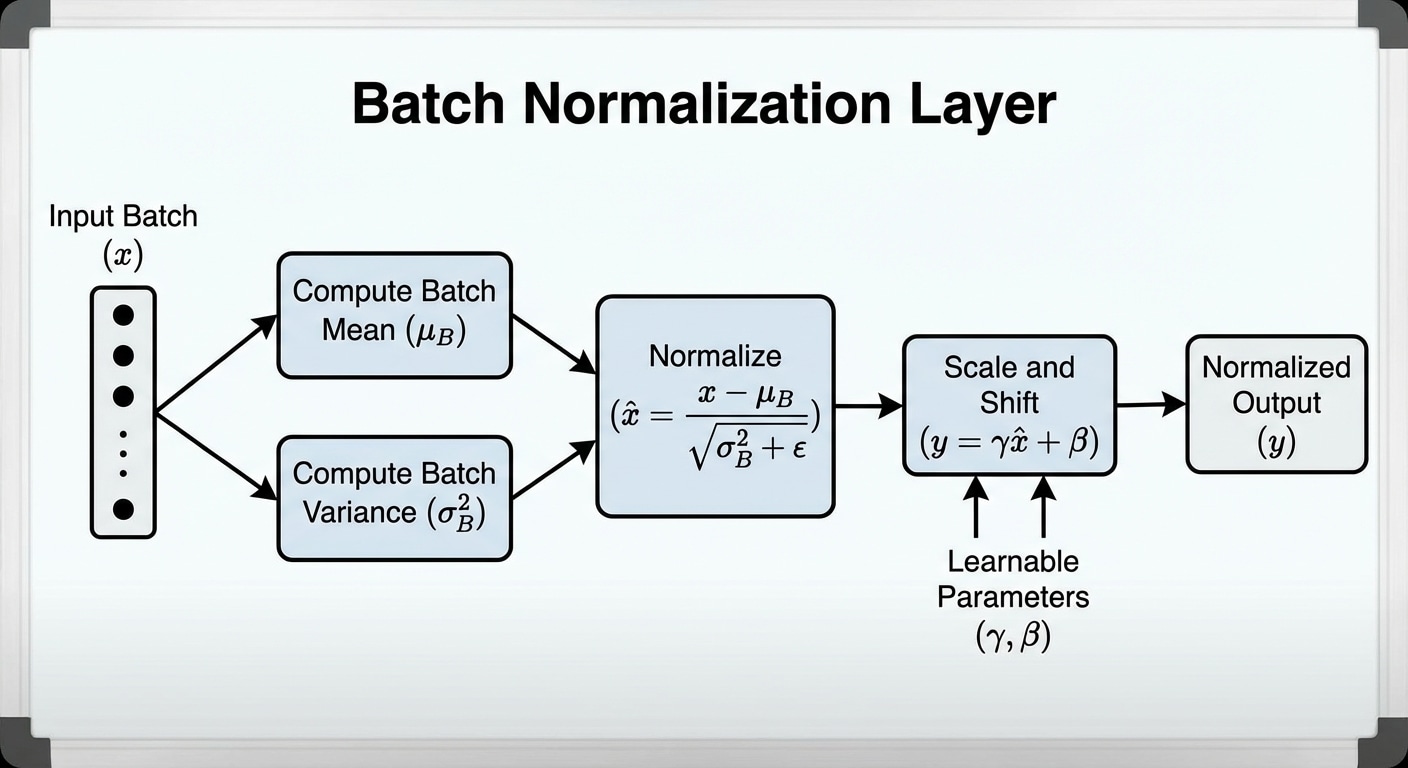
The pipeline involves preprocessing inputs (tokenizing text, resizing images, normalising values), running the forward pass through model layers, and postprocessing outputs (decoding tokens, formatting responses, applying thresholds). Each stage offers optimisation opportunities.
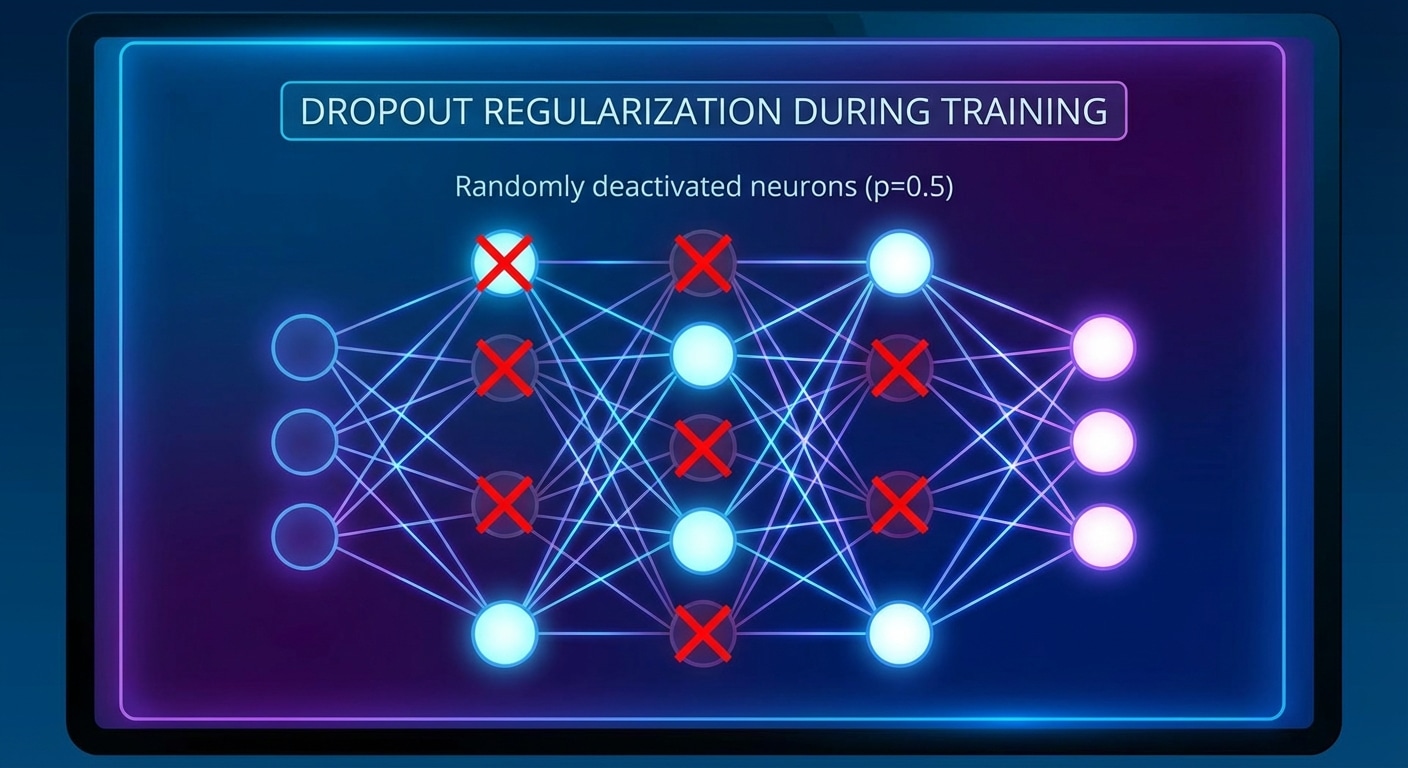
Common optimisations include quantization (reducing precision from FP32 to INT8), pruning (removing unimportant weights), distillation (training smaller models to mimic larger ones), and batching (processing multiple inputs together for GPU efficiency).
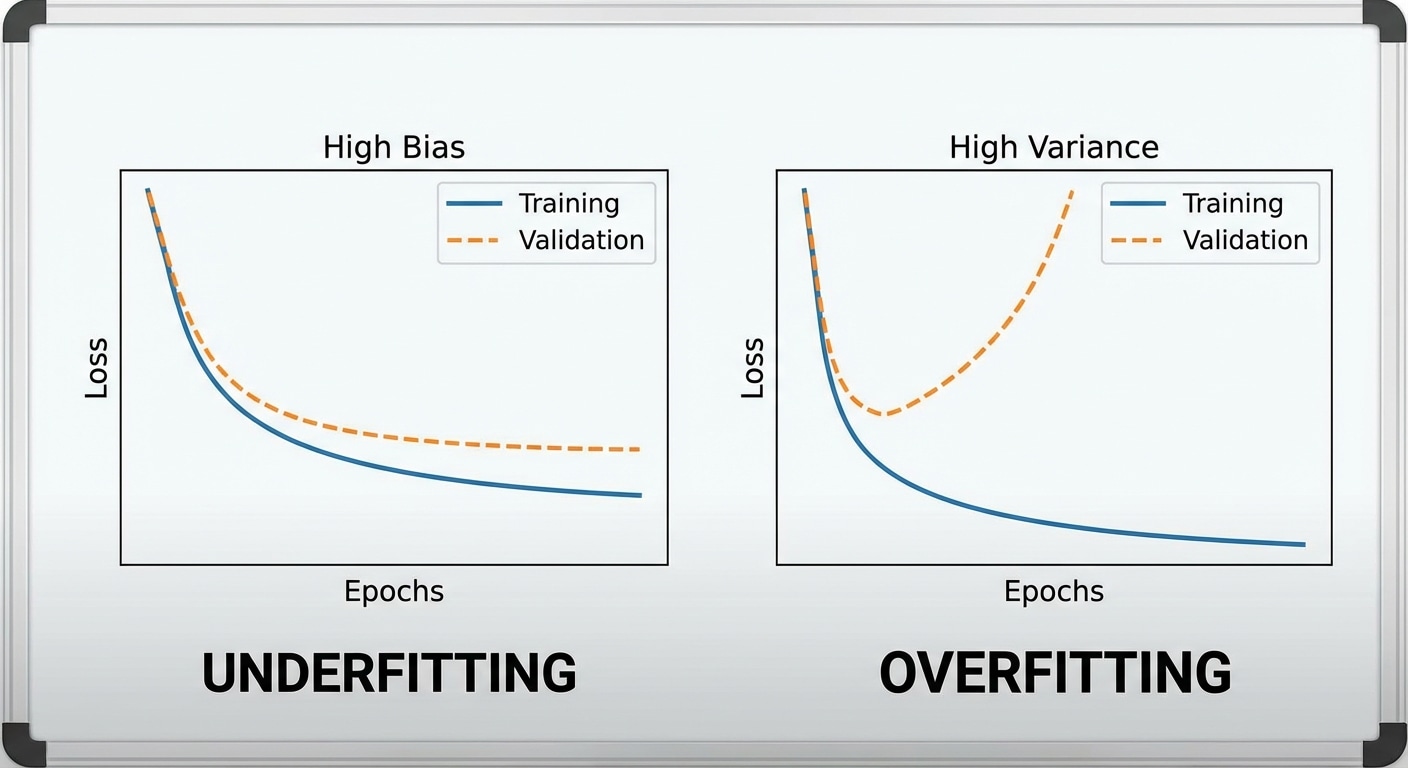
Latency considerations matter for user experience. First token latency determines perceived responsiveness. Tokens per second affects total generation time. For production systems, balance quality against speed based on your specific use case and user expectations.