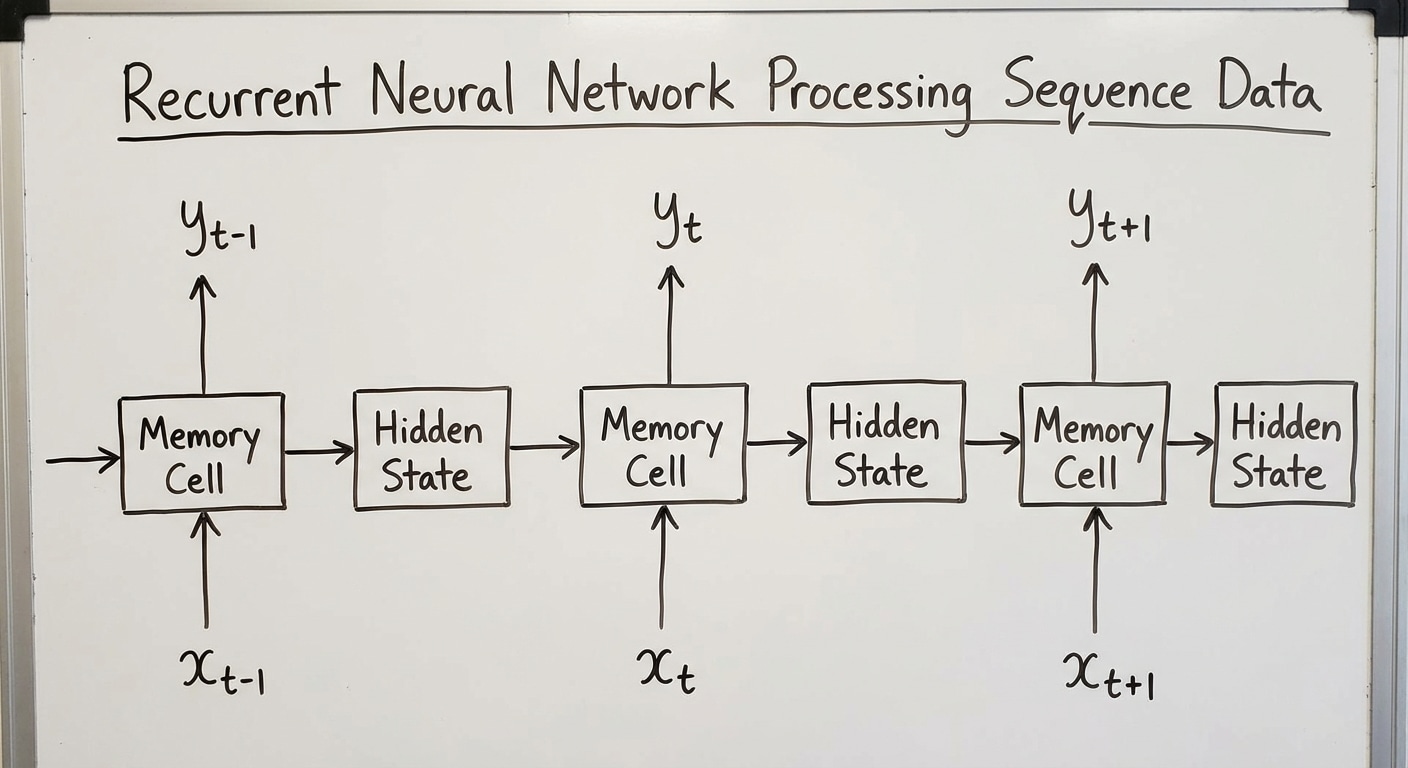
Recurrent Neural Networks: Processing Sequences
RNNs were designed for sequential data – text, time series, audio, and video. Unlike feedforward networks that process fixed-size inputs, RNNs maintain a hidden state that acts as memory, allowing information to persist across the sequence and enabling context-aware processing.
At each timestep, the hidden state combines the previous state with new input through learned transformations. This recurrence creates a computational graph that unfolds through time, theoretically allowing information from early inputs to influence later processing indefinitely.
In practice, vanilla RNNs struggle with long sequences due to vanishing gradients. When backpropagating through many timesteps, gradients shrink exponentially, causing the network to forget early information. Exploding gradients present the opposite problem, causing training instability.
While largely superseded by Transformers for most applications, understanding RNNs remains valuable. They introduced key concepts like sequence modeling and temporal dependencies. LSTM and GRU variants solved the gradient problems, and some real-time applications still benefit from RNNs streaming nature.
