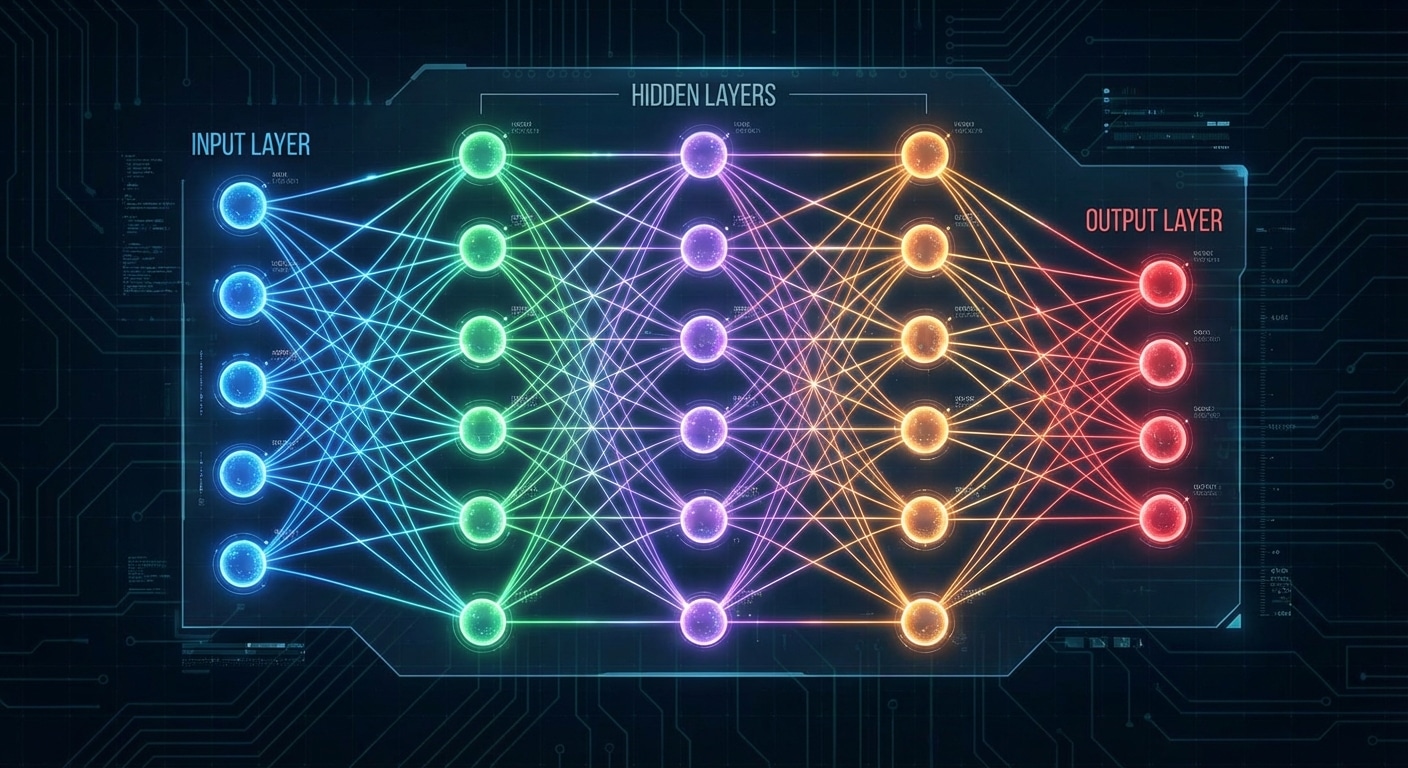
What is a Neural Network?
A neural network is a computational model inspired by the biological structure of the human brain. At its core, it consists of interconnected nodes called neurons, organized into distinct layers that process information hierarchically. These artificial neurons receive inputs, apply mathematical transformations, and produce outputs that feed into subsequent layers, creating a powerful system capable of learning complex patterns.
The architecture consists of three fundamental layer types. The input layer receives raw data such as images or text. Hidden layers transform inputs through weighted sums and activation functions, gradually learning meaningful representations. The output layer produces the final result – a classification, prediction, or generated content.
Each connection between neurons carries a weight determining influence. During training, weights are adjusted using backpropagation to minimize prediction errors. The computation follows: output equals activation function applied to sum of inputs times weights plus bias. This simple operation repeated millions of times enables learning incredibly complex patterns.
Understanding this architecture is crucial for AI development. The depth and width of networks determine learning capacity. Proper initialization, regularization, and optimization ensure successful training whether building image classifiers, language models, or recommendation systems.
