There is a particular kind of modern disappointment that only happens on an Apple Silicon Mac. You have 16 GB of unified memory, your model file is “only” 11 GB on disk, LM Studio looks optimistic for a moment, and then the load fails like a Victorian gentleman fainting at the sight of a spreadsheet. The internet calls this “hidden VRAM”. That phrase is catchy, but it is also slightly nonsense. Your Mac does not have secret gamer VRAM tucked behind the wallpaper. What it has is a shared memory pool and a tunable guardrail for how much of that pool the GPU side of the system is allowed to wire down. Move the guardrail carefully and some local LLMs that previously refused to load will suddenly run. Move it carelessly and your machine turns into a very expensive beachball generator.
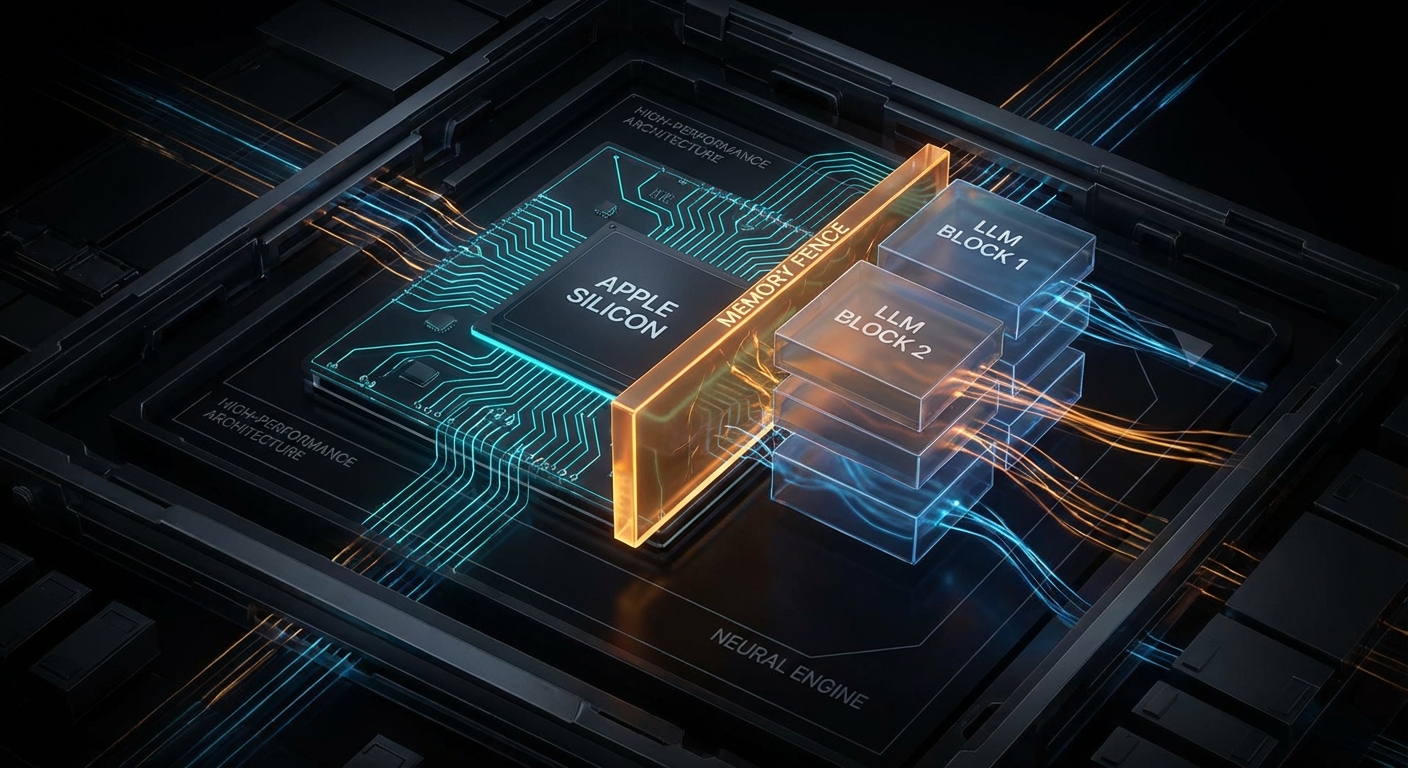
The practical knob is iogpu.wired_limit_mb. On this 16 GB Apple Silicon Mac, the default is still the default from the video:
$ sysctl iogpu.wired_limit_mb
iogpu.wired_limit_mb: 0That 0 means “use the system default policy”, not “unlimited”. For people running local models, that distinction matters. The interesting bit is that the policy is often conservative enough that a model which should fit on paper does not fit in practice once GPU allocations, KV cache, context length, the window server, and ordinary macOS overhead all take their cut. The result is a very familiar sentence: failed to load model.
What This Setting Actually Changes
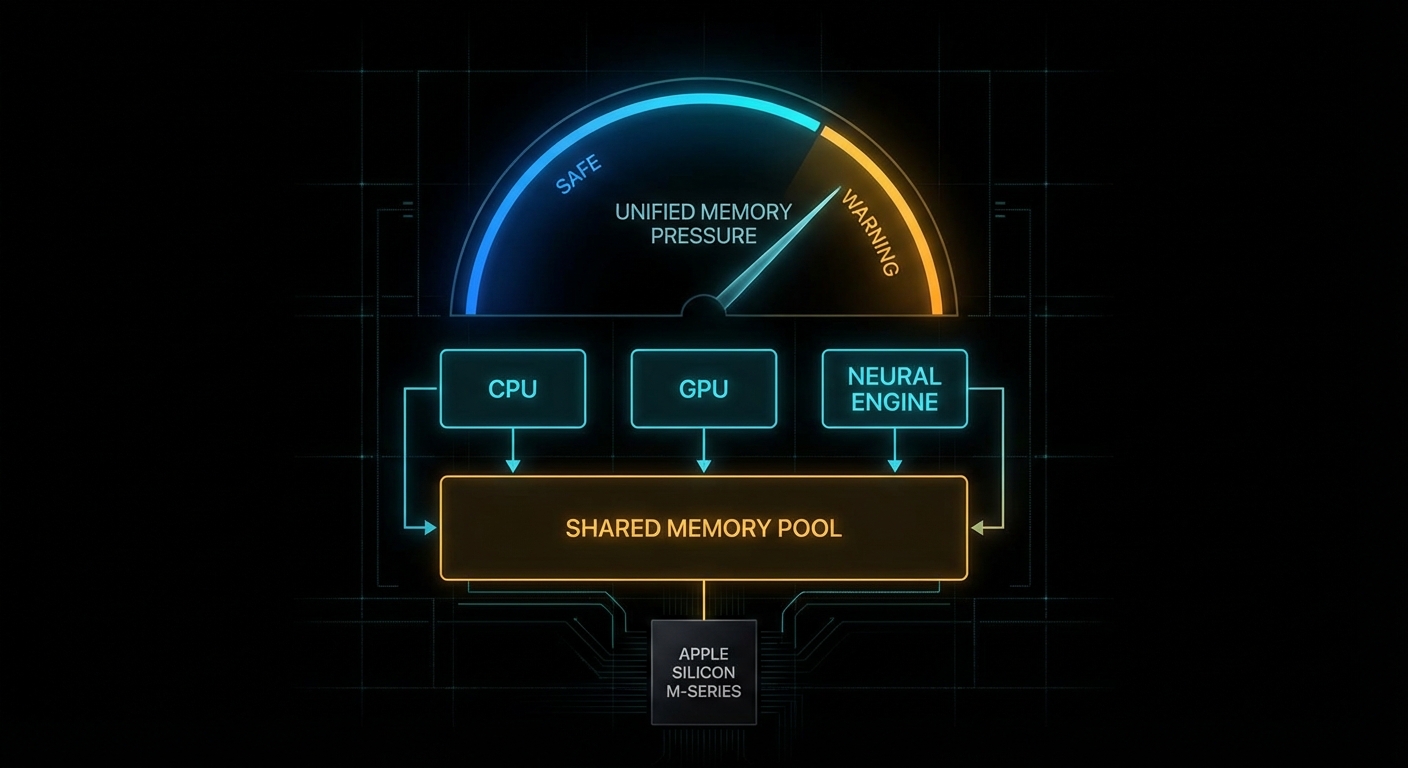
Apple’s architecture is the key to understanding why this works at all. Unlike a desktop PC with separate system RAM and discrete GPU VRAM, Apple Silicon uses one shared pool. Apple says it plainly:
“Apple GPUs have a unified memory model in which the CPU and the GPU share system memory.” – Apple Developer, Choosing a resource storage mode for Apple GPUs
That one sentence explains both the magic and the pain. The magic is that Apple laptops and minis can run surprisingly capable local models without a discrete GPU at all. The pain is that every byte you hand to GPU-backed inference is a byte you are not handing to the rest of the operating system. This is capacity planning, not sorcery. Kleppmann would recognise it instantly from Designing Data-Intensive Applications: one finite resource, several hungry consumers, and trouble whenever you pretend the budget is not real.
The lower-level Metal API exposes the same idea in more formal language. The property recommendedMaxWorkingSetSize is defined by Apple as:
“An approximation of how much memory, in bytes, this GPU device can allocate without affecting its runtime performance.” – Apple Developer, MTLDevice.recommendedMaxWorkingSetSize
Notice the wording: without affecting runtime performance. Apple is not promising a hard technical ceiling. It is describing a safety line. The iogpu.wired_limit_mb trick is, in effect, you saying: “thank you for the safety line, I would like to move it because I know what else is running on this machine”.
If you want to see the same concept from code rather than from a slider in LM Studio, a tiny Metal program can query the recommended budget directly:
import Metal
if let device = MTLCreateSystemDefaultDevice() {
let bytes = device.recommendedMaxWorkingSetSize
let gib = Double(bytes) / 1024.0 / 1024.0 / 1024.0
print(String(format: "Recommended GPU working set: %.2f GiB", gib))
}That value is the polite answer. iogpu.wired_limit_mb is how you become impolite, but hopefully still civilised.
Why Models Fail Before RAM Looks Full
Most newcomers look at the model file size and do schoolboy arithmetic: “11 GB file, 16 GB machine, therefore fine.” That works right up until reality arrives with a clipboard. Runtime memory use includes the model weights, the KV cache, backend allocations, context-length overhead, app overhead, and the rest of macOS. LM Studio explicitly gives you a way to inspect this before you pull the pin:
“Preview memory requirements before loading a model using
--estimate-only.” – LM Studio Docs, lms load
That is not a decorative feature. Use it. Also note LM Studio’s platform advice for macOS: 16GB+ RAM recommended, with 8 GB machines reserved for smaller models and modest contexts. The point is simple: local inference is not decided by model download size alone. It is decided by total live working set.
# Ask LM Studio for the memory estimate before loading
lms load --estimate-only openai/gpt-oss-20b
# Lower context if the estimate is close to the edge
lms load --estimate-only openai/gpt-oss-20b --context-length 4096
# If needed, reduce GPU usage rather than insisting on "max"
lms load openai/gpt-oss-20b --gpu 0.75 --context-length 4096That last point is underappreciated. Sometimes the right answer is not “raise the wired limit”. Sometimes the right answer is “pick a saner context length” or “run a smaller quant”. Engineers love hidden toggles because they feel like boss fights. In practice, boring budgeting wins.
The Failure Modes Nobody Mentions in the Thumbnail
The YouTube version of this story is understandably upbeat: type command, load bigger model, cue triumphant tokens per second. The real world deserves a sterner briefing. Three failure cases show up over and over.
Case 1: The Model File Fits, But the Live Working Set Does Not
The trigger is a model whose weights fit comfortably on disk, but whose runtime footprint exceeds the combined budget once context and cache are included.
# Bad mental model:
# "The GGUF is 11 GB, so my 16 GB Mac can obviously run it."
model_weights_gb = 11.2
kv_cache_gb = 1.8
backend_overhead_gb = 0.8
desktop_overhead_gb = 2.0
total_live_working_set = (
model_weights_gb +
kv_cache_gb +
backend_overhead_gb +
desktop_overhead_gb
)
print(total_live_working_set) # 15.8 GB, and we still have no safety marginWhat happens next is either a clean refusal to load or a dirty scramble into memory pressure. The correct pattern is to estimate first, shrink context if necessary, and accept that a lower-bit quant is often the smarter answer than a higher limit.
# Better approach: estimate, then choose the model tier that fits
lms load --estimate-only qwen/qwen3-8b
lms load --estimate-only openai/gpt-oss-20b --context-length 4096
# If the estimate is borderline, step down a tier
lms load qwen/qwen3-8b --gpu max --context-length 8192Case 2: You Raise the Limit So High That macOS Starts Fighting Back
This happens when you treat unified memory as if it were dedicated VRAM and leave the operating system too little breathing room. Headless Mac minis tolerate this better. A laptop with browsers, Finder, Spotlight, and a normal human life happening on it does not.
# Aggressive and often reckless on a 16 GB machine
sudo sysctl iogpu.wired_limit_mb=16000
# Then immediately try to load a borderline model
lms load openai/gpt-oss-20b --gpu maxThe machine may still succeed, which is what makes this dangerous. Success under orange memory pressure is not proof of wisdom. It is proof that you got away with it once. The better pattern is to leave deliberate headroom for the OS and keep a close eye on Activity Monitor while you test.
# A more conservative example for a 16 GB Mac
sudo sysctl iogpu.wired_limit_mb=14336
# Verify the setting
sysctl iogpu.wired_limit_mb
# Then test with a realistic context length
lms load openai/gpt-oss-20b --context-length 4096Case 3: You Optimise the Wrong Thing and Ignore Context Length
A surprisingly common mistake is to chase the biggest possible model whilst leaving an unnecessarily large context window enabled. KV cache is not free. A smaller context often buys you more stability than another dramatic sysctl ever will.
# Bad: max everything, then act surprised
lms load some-14b-model --gpu max --context-length 32768
# Better: fit the workload, not your ego
lms load some-14b-model --gpu max --context-length 4096
lms load some-8b-model --gpu max --context-length 8192This is the computing equivalent of bringing a grand piano to a pub quiz. Impressive, yes. Appropriate, no.
How to Tune It Without Turning Your Mac Into a Toaster
The safe way to use this setting is incremental, reversible, and boring. Those are good qualities in systems work. Start from default, raise in steps, test one model at a time, and watch memory pressure rather than vibes.
- Check the current value. If it is
0, you are on the system default policy. - Pick a target that still leaves real headroom. On a 16 GB machine, 14 GB is already adventurous. On a dedicated headless box, you can be bolder.
- Restart the inference app. Tools like LM Studio need to re-detect the budget.
- Load with a realistic context length. Do not benchmark recklessness.
- Reset to default if the machine becomes unpleasant. A responsive Mac beats a heroic screenshot.
# 1. Inspect current policy
sysctl iogpu.wired_limit_mb
# 2. Raise cautiously
sudo sysctl iogpu.wired_limit_mb=12288
# 3. Test, observe, then step up if needed
sudo sysctl iogpu.wired_limit_mb=14336
# 4. Return to default policy
sudo sysctl iogpu.wired_limit_mb=0If you truly need this on every boot, automate it like any other operational setting. Treat it as host configuration, not as a ritual you half-remember from a video. But also ask the adult question first: if you need a startup hack to run the model comfortably, should you really be running that model on this machine?
The second practical tool is estimation. Run the estimator before the load, not after the error:
# Compare two candidates before wasting time
lms load --estimate-only qwen/qwen3-8b
lms load --estimate-only mistral-small-3.1-24b --context-length 4096
# Use the estimate to choose the smaller model or context
lms load qwen/qwen3-8b --gpu max --context-length 8192Which Models Actually Make Sense on Different Apple Silicon Macs
This is the section everybody really wants. Exact numbers depend on quant format, context length, backend behaviour, and what else the machine is doing. But the tiers below are realistic enough to save people from magical thinking.
| Mac memory tier | Comfortable local LLM tier | Possible with tuning | Usually a bad idea |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16 GB | 3B to 8B models, 12B class with modest context | Some 14B to 20B quants if you raise the limit and stay disciplined | Large context 20B+, 30B-class models during normal desktop use |
| 24 GB | 8B to 14B models, many 20B-class quants | Some 24B to 32B models with sensible context | Treating it like a 64 GB workstation |
| 32 GB to 48 GB | 14B to 32B models comfortably, larger contexts for practical work | Some 70B quants on the upper end, especially on dedicated machines | Huge models plus giant context plus desktop multitasking |
| 64 GB and above | 30B to 70B-class quants become genuinely usable | Aggressive large-model experimentation on headless or dedicated Macs | Assuming every app uses memory exactly the same way |
If you want a one-line rule of thumb, it is this: on a 16 GB machine, think “excellent 7B to 8B box, adventurous 14B box, occasional 20B parlour trick”. On a 24 GB or 32 GB machine, the world gets much nicer. On a 64 GB+ Mac Studio, the conversation changes from “can I load this?” to “is the speed good enough for the inconvenience?”
Also remember that smaller, better-tuned models often beat larger awkward ones for day-to-day coding, search, summarisation, and chat. A responsive 8B or 14B model you actually use is more valuable than a 20B model that only runs when the stars align and Chrome is closed.
# Practical workflow: compare candidates before downloading your dignity away
lms load --estimate-only qwen/qwen3-4b
lms load --estimate-only qwen/qwen3-8b
lms load --estimate-only openai/gpt-oss-20b --context-length 4096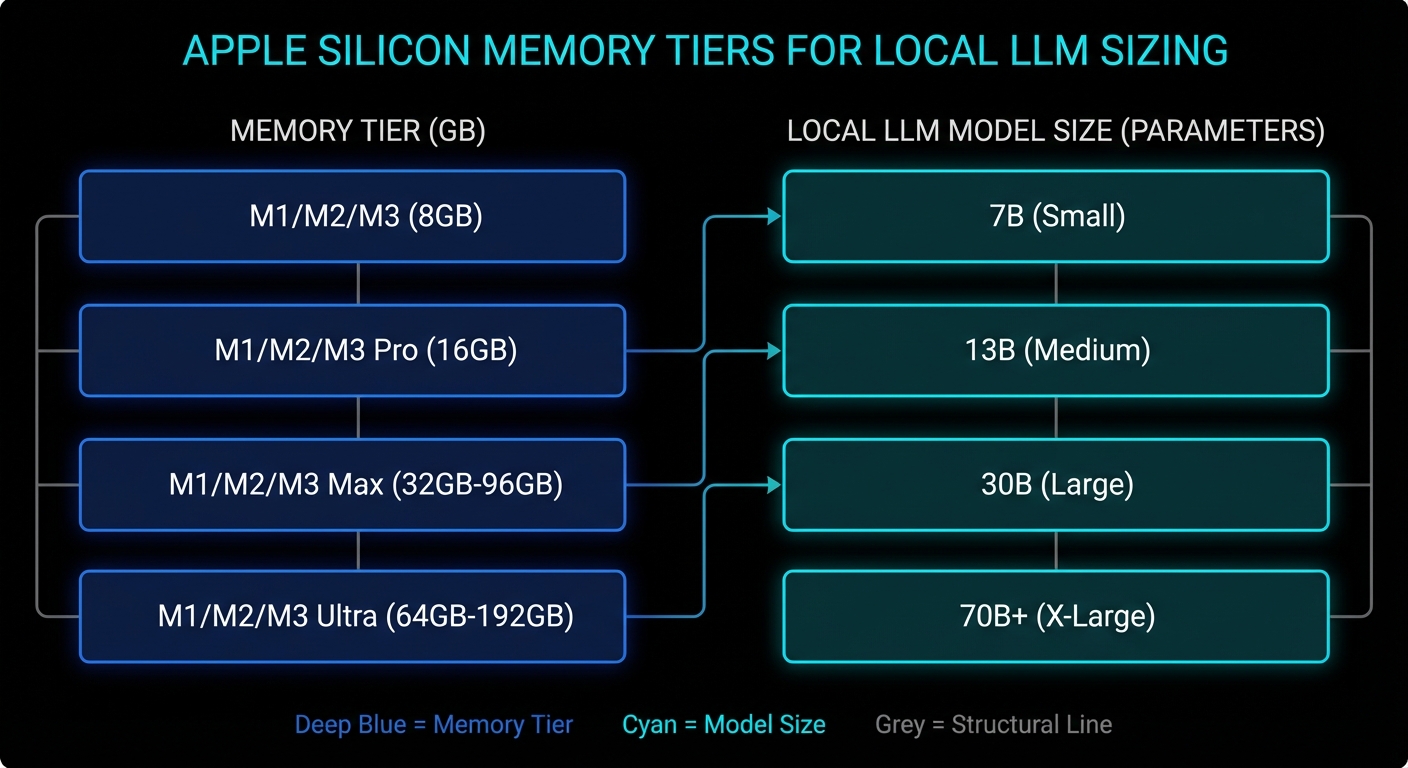
When the Default Setting Is Actually Fine
The balanced answer is that the default exists for good reasons. If your Mac is a general-purpose laptop, if you care about battery life and responsiveness, if you run multiple heavy apps at once, or if your local LLM work is mostly 7B to 8B models, leave the setting alone. The system default is often the correct trade-off.
This is also true if your workload is bursty rather than continuous. For occasional summarisation, coding assistance, or local RAG over documents, it is usually better to pick a slightly smaller model and preserve the machine’s overall behaviour. The hidden cost of “bigger model at any price” is that you stop trusting the computer. Once a laptop feels brittle, you use it less. That is bad engineering and worse ergonomics.
There is another subtle point. The wired-limit trick helps most when the machine is effectively dedicated to inference: a headless Mac mini, a quiet box on the shelf, a Mac Studio cluster, or a desktop session where you are willing to treat inference as the primary job. The closer your Mac is to a single-purpose appliance, the more sense this tweak makes.
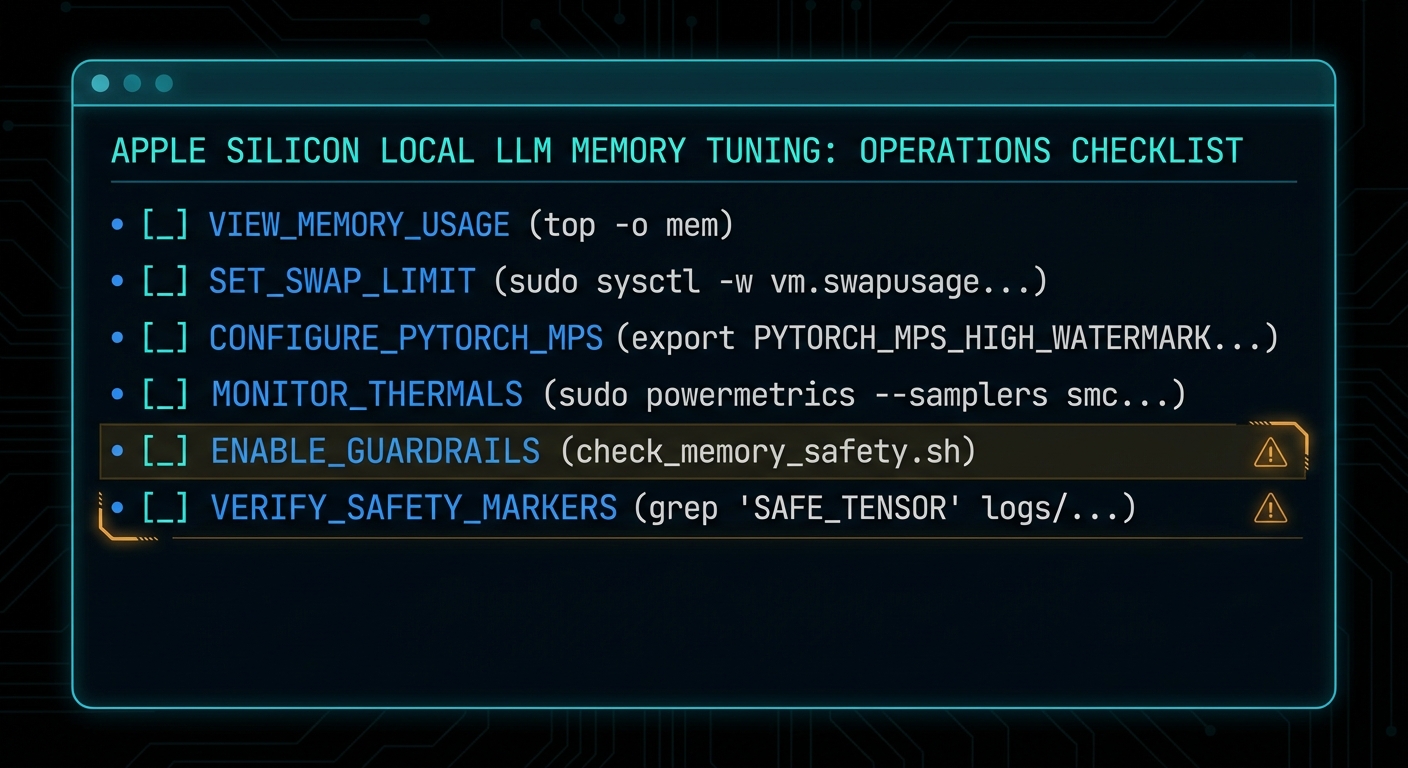
What To Check Right Now
- Check the current policy: run
sysctl iogpu.wired_limit_mband confirm whether you are on the default setting. - Estimate before loading: use
lms load --estimate-onlyso you know the model’s live working set before you commit. - Audit context length: if you are using 16k or 32k context by habit, ask whether 4k or 8k would do the same job.
- Watch memory pressure, not just free RAM: Activity Monitor tells you more truth than a single headline number.
- Leave deliberate headroom: a model that barely runs is not a production setup, it is a stunt.
- Reset when testing is over:
sudo sysctl iogpu.wired_limit_mb=0is a perfectly respectable ending.
The honest headline, then, is better than the clickbait one. Your Mac does not have hidden VRAM waiting to be unlocked like a cheat code in a 1998 driving game. What it has is unified memory, a conservative GPU working-set policy, and enough flexibility that informed users can rebalance the machine for local inference. That is genuinely useful. It is also exactly the sort of useful that punishes people who confuse “possible” with “free”.
Video Attribution
This article was inspired by Alex Ziskind’s video on adjusting the GPU wired-memory limit for local LLM use on Apple Silicon Macs. The video is worth watching for the quick demonstration, particularly if you want to see the behaviour in LM Studio before you touch your own machine.
Original video: Your Mac Has Hidden VRAM… Here’s How to Unlock It by Alex Ziskind.
nJoy 😉