Batch Normalization: Stabilizing Training
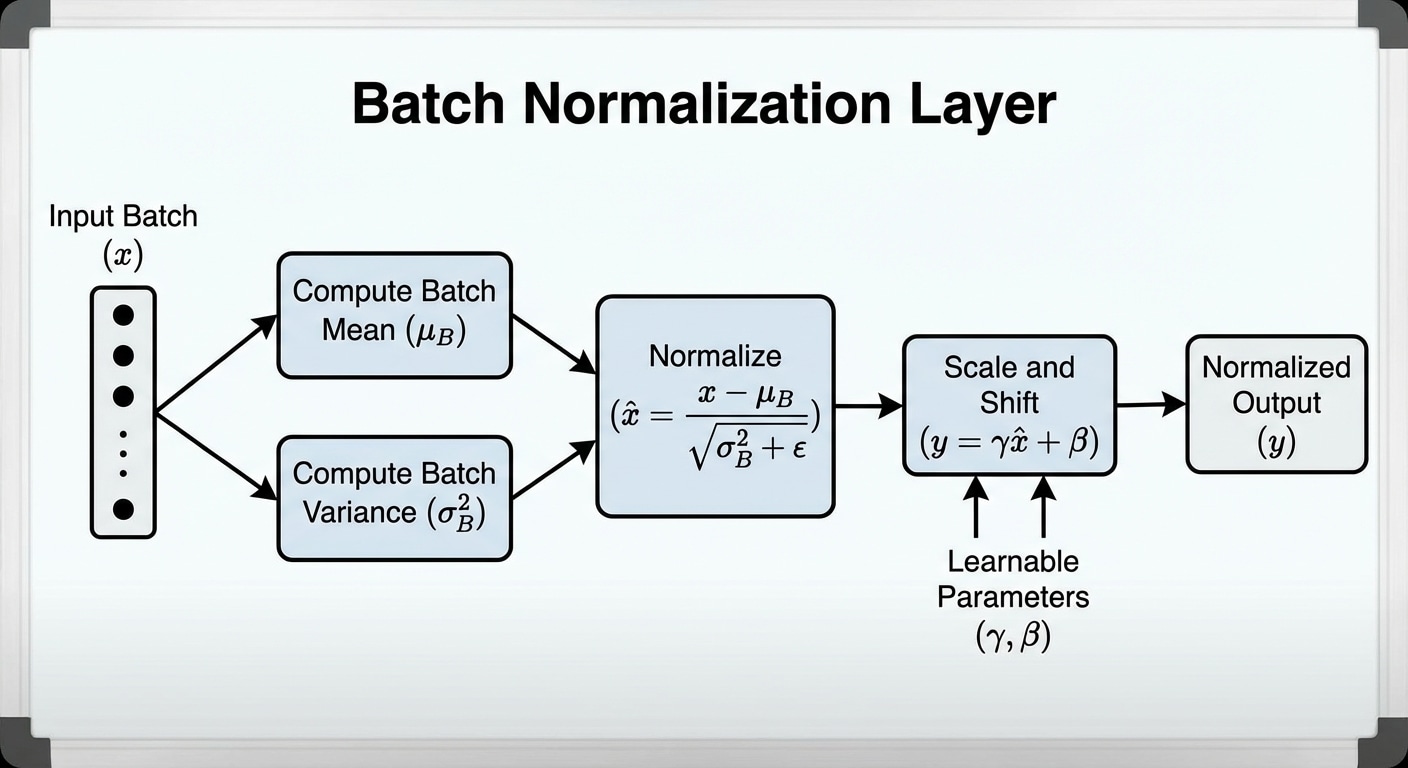
Batch normalization dramatically improved training stability and speed when introduced in 2015. By normalizing layer inputs, it reduces internal covariate shift and allows much higher learning rates, accelerating convergence significantly.
For each mini-batch, BatchNorm calculates mean and variance of activations, normalizes them to zero mean and unit variance, then applies learnable scale and shift parameters. This standardization stabilizes the distribution of inputs to each layer.
Benefits extend beyond training speed. BatchNorm acts as a regularizer due to noise from batch statistics, often reducing or eliminating the need for dropout. It also reduces sensitivity to weight initialization, making networks easier to train.
Layer Normalization offers an alternative for Transformers, normalizing across features instead of batch dimension. This works with any batch size and is essential for sequence models where batch statistics can be noisy.
